With Data Analytics, IoT, & AI, Gorakhpur Builds Predictive, Real-Time Monsoon Resilience
Gorakhpur’s Urban Flood Management System uses AI-based forecasting, IoT sensors, and automated pumps to shift the city from reactive flood relief to proactive preparedness. With reliable early warnings, faster field deployment, and stronger citizen participation, the system has cut response times dramatically and improved overall efficiency by 65%, creating a more resilient and safer urban environment.
Updated on: 02 December 2025

Sector

Solution
Public Safety
Technology
IoT

State of Origin
Impact Metrics
Response time reduced
from 10–12 hours to 1.5–2 hours.
65% improvement
strengthening real-time field coordination and reducing flood-related damage.
80% predictions accurate
for rain and waterlogging, allowing teams to act early and prevent flooding.
95% coverage
for pre-monsoon drain cleaning achieved.
For decades, Gorakhpur’s geography and rapid urbanisation produced severe inundation across low-lying wards. Ageing drainage networks, limited gradient, and the rise of impermeable surfaces resulted in recurrent waterlogging lasting days, causing damage to homes, disruption of mobility, and heightened risk of vector-borne diseases. Municipal responses were often delayed by 10–12 hours, constrained by manual pump operations, fragmented field coordination, and the absence of real-time information.
Recognising the systemic nature of this challenge, the Municipal Corporation initiated a structured reform combining predictive analytics, standard operating procedures, infrastructure automation, and community participation.
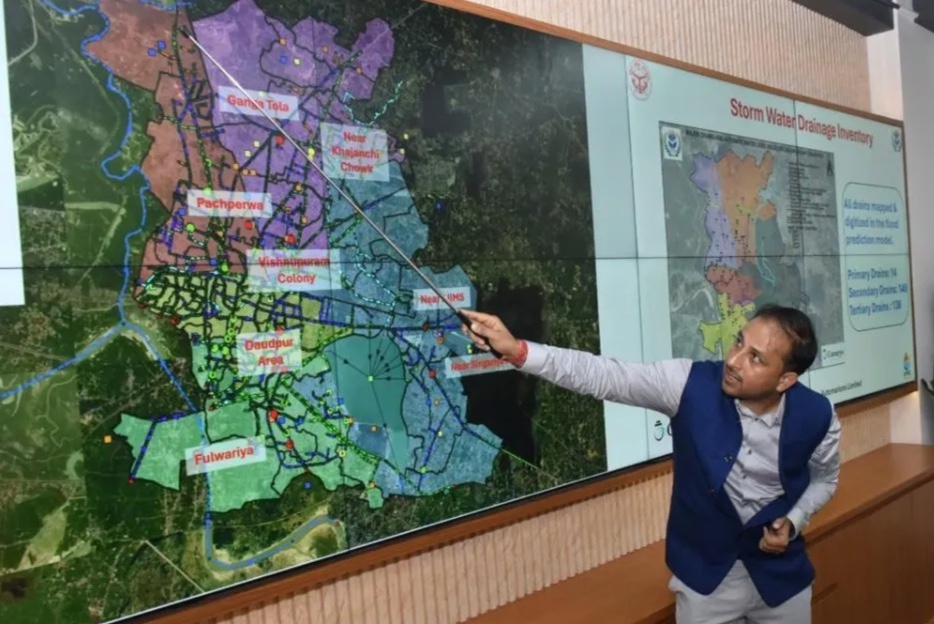
Gorakhpur’s Urban Flood Management System (UFMS), implemented in 2023–24 by the Gorakhpur Municipal Corporation in partnership with Canarys Automations, represents a comprehensive integration of hydrometeorological forecasting, IoT-enabled monitoring, automated pump control, and citizen-centric communication. Designed to address chronic monsoon flooding in a low-lying, saucer-shaped city, the system was conceptualised and led by municipal officials under Municipal Commissioner Gaurav Singh Sogarwal and Mayor Dr Manglesh Kumar Srivastava, with technological development driven by Canarys CEO Sheshadri Srinivas and his field engineering and telemetry teams. The objective was clear—transition from a reactive, delayed flood-response model to a predictive, data-driven, and operationally coordinated system capable of protecting lives, property, and essential services.
Designing a city-wide, intelligence-led flood management ecosystem
The Urban Flood Management Centre (UFMC) established by Canarys serves as the operational nucleus of the system. It integrates:
-
Early Warning System (EWS) using AI-based rainfall forecasting and ward-level flood prediction up to 24 hours in advance.
-
Decision Support System (DSS) combining weather data, live rainfall feeds, water-level sensors, drainage flow measurements, and historical flood records to guide pre-emptive and real-time action.
-
SCADA-based pump automation, enabling remote pump operation across 21 of 25 pumping stations to reduce delays and human error.
-
Field engineering support, with Canarys staff embedded inside the control room and deployed across hotspots during rainfall events to provide on-ground verification and rapid intervention.
-
Community-facing mechanisms, including a grievance portal, helpline, and the upcoming Varuna mobile app for citizen-sourced alerts.
The operational workflow is built on three interlinked pillars—Predict, Prepare, Protect. Prediction outputs guide pre-rain drain cleaning, pump maintenance, field deployment, and emergency staffing. During rainfall, real-time dashboards, walkie-talkie networks, WhatsApp-based coordination, and automated pumps enable rapid response. Citizen complaints feed directly into UFMC operations, facilitating targeted interventions.
Implementation timeline
From April 2024 onward, the project progressed through a structured sequence: conceptualisation and goal-setting; hydrometeorological modelling; installation of IoT sensors and cloud analytics; establishment of UFMC; pump automation through SCADA; and roll-out of citizen-engagement channels. By late 2024–early 2025, predictive models were refined, operational protocols institutionalised, and community participation scaled, enabling Gorakhpur’s shift to a proactive flood-resilience model.
Impact and outcomes
Within the first monsoon cycle of implementation, Gorakhpur documented significant improvements:
-
Response time reduced from 10–12 hours to 1.5–2 hours.
-
Pump downtime decreased by over 60%.
-
Pre-monsoon drain cleaning achieved 95% coverage.
-
Forecast accuracy for rainfall and waterlogging exceeded 80% at 24-hour horizons.
-
250+ citizen complaints addressed, with 70% resolved within hours.
-
Overall system efficiency improved by 65%, strengthening real-time field coordination and reducing flood-related damage.
Residents in vulnerable zones reported significantly reduced water stagnation, quicker relief, and improved municipal responsiveness—signalling a shift from reactive crisis management to structured preparedness.
Implications for national safety and security
Urban flooding is not only a civic problem—it is a national safety and security concern. Floods disrupt transport corridors, damage critical infrastructure, weaken public health systems, and strain emergency services. Gorakhpur’s UFMS demonstrates how data-driven forecasting, IoT-enabled automation, coordinated field deployment, and citizen participation can substantially reduce urban vulnerability. Scaled across Indian cities, such systems can safeguard essential infrastructure, protect low-income and high-risk settlements, support climate-resilient urban planning, and enhance disaster-readiness of municipal institutions. In border states and strategic districts, similar platforms can strengthen continuity of governance and reduce disruptions that adversaries or natural hazards could exploit. Gorakhpur’s model thus provides a replicable blueprint for climate-resilient, secure, and responsive urban management across India.
Share Your Story Today, Shape Viksit Bharat Tomorrow
Got an idea, innovation, or experience that's making a difference? Share your story now and ignite India's transformation because your voice can drive the future forward!
Handpicked stories tailored just for you
Explore stories that inspire, inform, and ignite new ideas across tech, innovation, and real-world impact


AI-Enabled Gynaecological Care Expands Access to 400,000+ Women Across India
Pinky Promise is a chat-first, AI-assisted women’s healthcare platform delivering affordable, confidential gynaecological care at scale. Founded in 2022, it...
Read More

